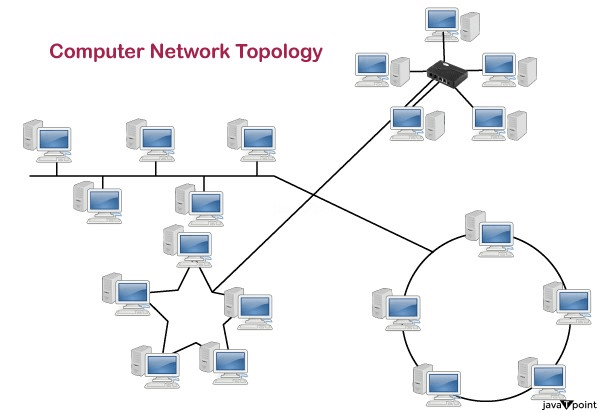
Topology defines the structure of the network of how all the components are interconnected to each other. There are two types of topology: physical and logical topology.
Physical topology is the geometric representation of all the nodes in a network.
Bus Topology
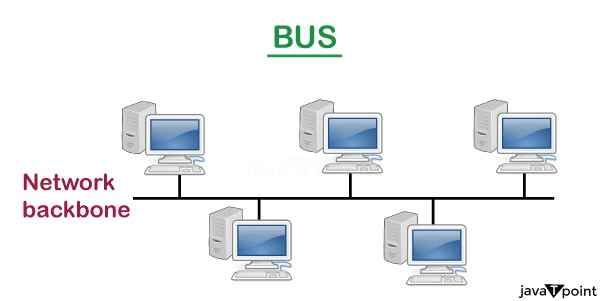
- The bus topology is designed in such a way that all the stations are connected through a single cable known as a backbone cable.
- Each node is either connected to the backbone cable by drop cable or directly connected to the backbone cable.
- When a node wants to send a message over the network, it puts a message over the network. All the stations available in the network will receive the message whether it has been addressed or not.
- The backbone cable is considered as a "single lane" through which the message is broadcast to all the stations.
Advantages of Bus topology:
- Low-cost cable: In bus topology, nodes are directly connected to the cable without passing through a hub. Therefore, the initial cost of installation is low.
- Moderate data speeds: Coaxial or twisted pair cables are mainly used in bus-based networks that support upto 10 Mbps.
- Familiar technology: Bus topology is a familiar technology as the installation and troubleshooting techniques are well known, and hardware components are easily available.
- Limited failure: A failure in one node will not have any effect on other nodes.
Ring Topology
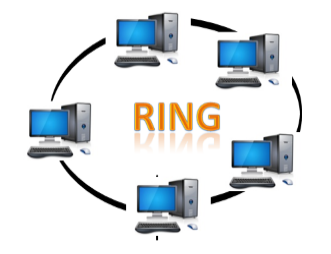
- Ring topology is like a bus topology, but with connected ends.
- The node that receives the message from the previous computer will retransmit to the next node.
- The data flows in one direction, i.e., it is unidirectional.
- The data flows in a single loop continuously known as an endless loop.
- It has no terminated ends, i.e., each node is connected to other node and having no termination point.
- The data in a ring topology flow in a clockwise direction.
Star Topology
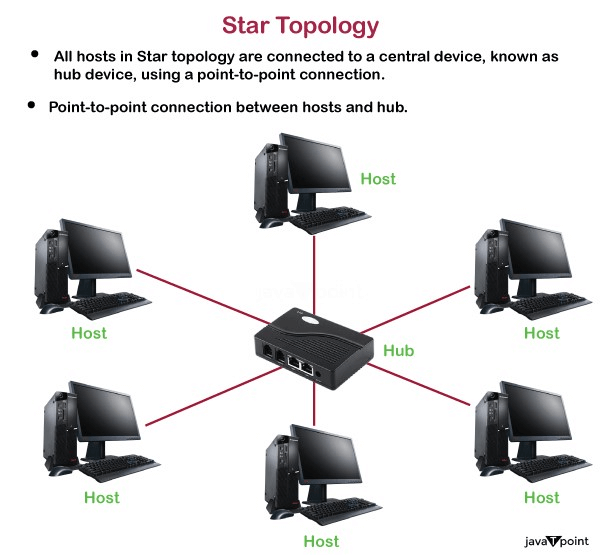
- Star topology is an arrangement of the network in which every node is connected to the central hub, switch or a central computer.
- The central computer is known as a server, and the peripheral devices attached to the server are known as clients.
- Coaxial cable or RJ-45 cables are used to connect the computers.
- Hubs or Switches are mainly used as connection devices in a physical star topology.
- Star topology is the most popular topology in network implementation.
Tree topology
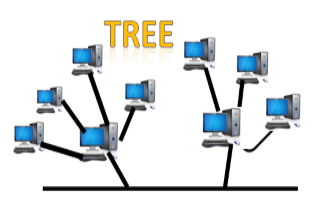
- Tree topology combines the characteristics of bus topology and star topology.
- A tree topology is a type of structure in which all the computers are connected with each other in hierarchical fashion.
- The top-most node in tree topology is known as a root node, and all other nodes are the descendants of the root node.
- There is only one path exists between two nodes for the data transmission. Thus, it forms a parent-child hierarchy.
Mesh topology
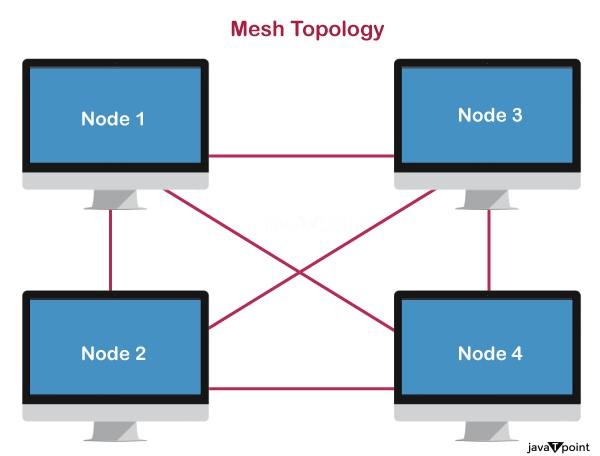
- Mesh technology is an arrangement of the network in which computers are interconnected with each other through various redundant connections.
- There are multiple paths from one computer to another computer.
- It does not contain the switch, hub or any central computer which acts as a central point of communication.
- The Internet is an example of the mesh topology.
- Mesh topology is mainly used for WAN implementations where communication failures are a critical concern.
- Mesh topology is mainly used for wireless networks.
- Mesh topology can be formed by using the formula:
Number of cables = (n*(n-1))/2;
Hybrid Topology
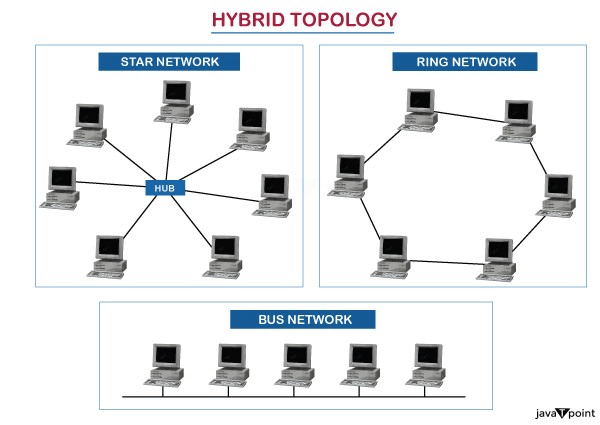
- The combination of various different topologies is known as Hybrid topology.
- A Hybrid topology is a connection between different links and nodes to transfer the data.
- When two or more different topologies are combined together is termed as Hybrid topology and if similar topologies are connected with each other will not result in Hybrid topology. For example, if there exist a ring topology in one branch of ICICI bank and bus topology in another branch of ICICI bank, connecting these two topologies will result in Hybrid topology.